Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s rapidly paced, innovative world, the quality of fresh ideas and innovative problem-solving skills has been a highly valued requirement. This could be whether it was the necessity to deal with a work project, the launch of a new business, or just a way to think through personal challenges, brainstorming will unlock your genius.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art and science of brainstorming, how to enhance it with tools like mind mapping, and ways it can drive innovation and problem-solving.
What is Brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a group technique of creativity that was popularized by Alex Osborn way back in the 1940s. It is a method of producing many ideas in very little time. Its core idea lies in generating quantity over quality at this point in the creative process, allowing participants to give free expression without judgment or criticism. In this regard, this method, though basic, provides the foundation for innovative thinking and effective problem-solving.
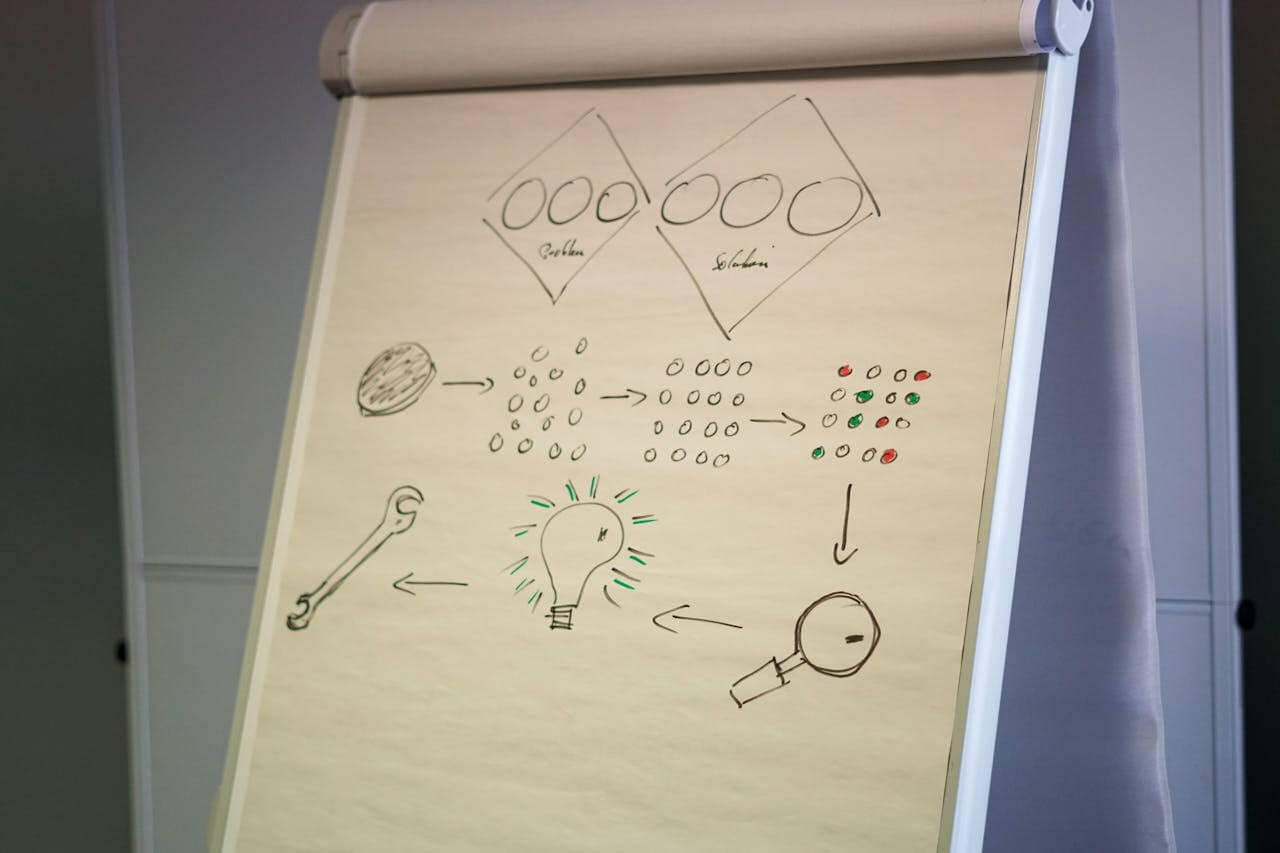
Why is Brainstorming Important?
Icts innovation: It allows diverse ideas to stimulate the mind for incubation of innovation.
Supports better problem-solving: Sowing multiple perspectives helps probe deeper into challenges.
Fosters Teamwork: Brainstorming is a teamwork activity by which people develop collective intelligence.
The Science Behind Brainstorming
How the Brain Works During Ideation
When brainstorming, your brain’s creative (right) hemisphere and logical (left) hemisphere work in tandem. The creative side generates ideas, while the logical side evaluates their feasibility. Techniques like mind mapping and lateral thinking help in bridging these hemispheres, ensuring optimal brain function.
The Role of Dopamine: This will bring about a certain level of dopamine balance as the “feel good” neurotransmitter is stimulated. The released chemical leads to an increased focus, creativity, and motivation, therefore effective brainstorming both effective and fun.
The Technique Process
Objective Setting: Identify clearly what the problem is or what’s the goal. Having a well-defined question or challenge that will provide the necessary steering to the brainstorming session.
The Rules
Don’t Criticise or Judge.
Let Loose: Encourage wild ideas.
Quantity over Quality.
Build on Others’ Ideas.
Choose the Right Environment: Creativity flourishes very well in a calm, concentrated environment. Paper and non-paper visual aids in the form of whiteboards or colorful, shiny sticky notes make a session engaging.
Tools and Techniques: Techniques, mind maps, SCAMPER, reverse brainstorming help to structure and enrich your sessions.
Ideation Refining: After the Ideation
session, ideas need to be reviewed and developed. Similar ideas need to be grouped and duplicates eliminated, along with discussion about their feasibility too.
Mind Mapping: A Game-Changer Mind mapping is a visual Ideation technique used to organize thoughts and ideas. Brainchild of Tony Buzan, it is a diagrammatic creation where ideas radiate from a central concept.
How to Create a Mind Map
Write the central theme or problem in the middle of the page.
Draw branches for each category or sub-idea.
Add keywords, images, or symbols to each branch.
Use colors to differentiate ideas and add visual appeal.
Benefits of Mind Mapping
It encourages free association of ideas.
Easy and clear overview of complex subjects
Promotes creativity as well as the logics at the same time.
Ideation Techniques for Innovation
SCAMPER Method: Using a checklist of prompts (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Rearrange) to generate and improve ideas
Round-Robin Brainstorming:
Getting one idea from each participant: Everyone’s voice is heard.
This Ideation technique focuses on making questions about the problem rather than solutions. It encourages a deeper search. .
Rapid Ideation:
Set a timer and challenge participants to write as many ideas as they can within the time limit.
Brainwriting
Participants write down ideas and share them with each other, building on one another’s ideas.
Overcoming Brainstorming Challenges
Common Pitfalls
Groupthink: A dominant voice will stifle other ideas.
Fear of Judgment: Contributors will hesitate to discuss seemingly crazy ideas.
Lack of Focus: Sessions will quickly go off track without a clear goal in mind.
Solutions
Appoint a neutral facilitator to control the session.
Anonymous brainstorming tools, apps
Identify what should be done and how long it will take.
The Brainstorming in Problem Solving
Ideation is vital for dealing with difficult problems. The process is effective in bringing different opinions within a team to break down the issue and coming up with new solutions.

Procedure of Problem Solving through Ideation
Identify the cause of a problem by using the 5 Whys or a fishbone diagram.
Ideation possible answers.
Screen and rank ideas by impact and feasibility.
Implement and try out the selected solution.
Improving Brainstorming with Technology
Technology has transformed Ideation, offering opportunities to brainstorm more easily and efficiently. Some options include:
MindMeister: A good choice for collaborative mind mapping.
Miro: An online digital whiteboard for Ideation and collaboration.
Stormboard: Blends brainstorming functions with project management.
Trello: a plan for organizing and prioritizing ideas after brainstorming
Brainstorming for Personal Development
Just as Creative thinking is used by teams, it can also be applied by an individual. Personal brainstorming enables an individual to:
Set and accomplish individual goals.
Overcome daily problems.
Develop self-reflection and creativity.
Tips for Creative thinking Alone
Jot down ideas with a journal or digital note-taking apps.
Try random word association to stimulate the mind.
Find time to rest to prevent mental exhaustion.
Practical Applications of Creative thinking
Business Invention:
Google and IDEO rely on Ideation to create innovative products and services.
Education:
Students and teachers brainstorm creative solutions to classroom problems.
Healthcare:
Health care teams brainstorm to create treatment plans or enhance patient care.
Show Business:
Writers, directors, and game developers employ Creative thinking as a way of developing interesting storylines and concepts.
Ideation and Creativity: A Symbiotic Relationship
Creativity will blossom in environments where ideas are not judged but nurtured and explored. Creative thinking thus provides that environment. It is a free flow of thoughts that breaks mental barriers and induces out-of-the-box thinking.
The more one engages in brainstorming the greater is his mind’s ability to spot opportunities and solutions in his life.
Tips to Boost Creativity During Brainstorming
Take the Leap of Faith: Try ideas which a little bit weird or risk-taking.
Use Humor, Roleplay, or Absurdity: Playfully try to stimulate the imagination.
Cross-Pollinate Knowledge: Look at how other industries solve the problem and innovate around it.
Look for Solutions Divergently: Actively seek multiple solutions to the same problem, but even if they appear contradictory.
Brainstorming Strategy For Strategic Planning
The benefit of brainstorming lies not only in the generation of ideas but also at the strategic planning levels. It can make designing a marketing campaign or formulating long-term goals or even resource allocation easier.
Steps in Strategic Brainstorming
Establish Clear Objective: Define what success looks like for your strategy.
Gather Data: Use research and analytics to inform your Ideation session.
Scan Scenarios: Brainstorm multiple approaches to your objective, including best-case and worst-case scenarios.
Actions to Prioritize: Rank the ideas and target towards short-term and long-term objectives.
Leveraging Diversity in Brainstorming
When diverse teams are involved, Ideation sessions tend to be richer in content. People belonging to different walks of life, having different experiences, and possessing varying sets of skills bring forth novel views that might lead to fantastic breakthroughs.
How to Leverage Diversity
Cross-Functional Teams: Bring people from different departments or fields.
Promote Inclusive Participation: Ensure that everybody’s input is encouraged and valued.
Respect Cultural Differences: Abstain and value varying ways of thinking and solving.
The Psychology of Creative thinking
Knowledge of the psychological variables associated with Creative thinking can make it work more effectively.
Psychological Inhibitors
Fear of Rejection: Members of a group do not want to contribute ideas for the fear of them being rejected.
Confirmation Bias: People tend to choose familiar over innovative solutions
Mental Exhausting: The brain gets exhausted with attention and creativity over long sessions
Psychological Enhancers
Positive Reinforcement: Praise and celebrate any contribution; great or small.
It’s a Safe Space: Stress to all that no ideas are wrong during brainstorming
Timed Intervals: Use short and timed sprints for energy and focus
Measuring the Success of a Brainstorming Session
It is highly essential to measure the outcome of your Ideation so that it brings value. A good session does not only count the sheer number of ideas but also the strength of them and how applicable they can be.
Metrics to Measure
Idea Quantity: Measure the total number of ideas.
Idea Diversity: Measure the range of ideas—how diverse and innovative they are.
Implementation Rate: How many ideas are there that become an actionable plan.
Team Engagement: Gauge the extent of participation and excitement during the session.
Case Studies: Brainstorming in Action
1. Origin of Sticky Note
Coming from Creative thinking, product concepts started coming out from the minds of 3M’s workers to pursue a “flop” experiment-the development of Post-it Notes, which eventually became global due to the company’s willingness to brainstorm.
2. Pixar’s Brain Trust
The Brain Trust is a collective Creative thinking model that Pixar uses, whereby filmmakers submit ideas in order to receive constructive criticism from peers; some of the most loved animated films were made through this method.
3. NASA’s Solution Groups
When the infamous mishap occurred on Apollo 13, NASA used the brainstorming that their team came up with quickly and creatively to rescue the astronauts before landing them safely on Earth.
Growing through Brainstorming
Brainstorming is not just professional-it can also be applied for personal development. Transferring Creative thinking techniques to everyday life, you can identify what should be done differently, set up targets, and discover your unrealized strengths.

Private Applications
Planning a Career: Planning possible careers, career growth methodologies
Habits Creation: Imagination of positive or negative habits and how to create them or destroy those.
Life Choices: Pros and cons assessment, solution finding, and deciding the possibilities related to major life decisions.
Conclusion Mastering the Art of Brainstorming
Creative thinking is more than just a technique-it’s a way of thinking. It involves creativity, not valuing individualism, but collaboration and curiosity combined with open-mindedness when approaching the challenges at hand. Mastering Creative thinking can transform the way you think and act when solving problems, innovating a product, or planning your next big move.
Important Takeaways
Creative thinking is a dynamic process that fuels creativity and innovation.
Mind mapping and SCAMPER heighten the techniques of Creative thinking for you.
Let go of those psychological blocks to initiate a fruitful Creative thinking culture.
Measuring the success of ideas and incorporating them in real life comes hand in hand with ideating them.
Unshackle the art of Creative thinking, and let your inner genius create momentous confidence and innovative ways to take on challenges. Start now, your next brilliant idea is just one brainstorm away!


