Table of Contents
Introduction
Eisenhower Matrix: How to Use Time Management for Perfect Work-Life Balance Living in a world where every day is a challenge between the rising demands of professional life and the urge for a good personal life, finding the right time management technique has become more crucial than ever.
The concept of work-life balance is not about dividing time between the two equally but managing tasks in such a way that one can live a healthy life without getting overwhelmed. All these balances are most effectively achieved by utilizing a simple, yet powerful method known as the Eisenhower Matrix. It is named after Dwight D. Eisenhower, the 34th President of the United States, who was widely known for his incredible productivity.
What is the Eisenhower Matrix?
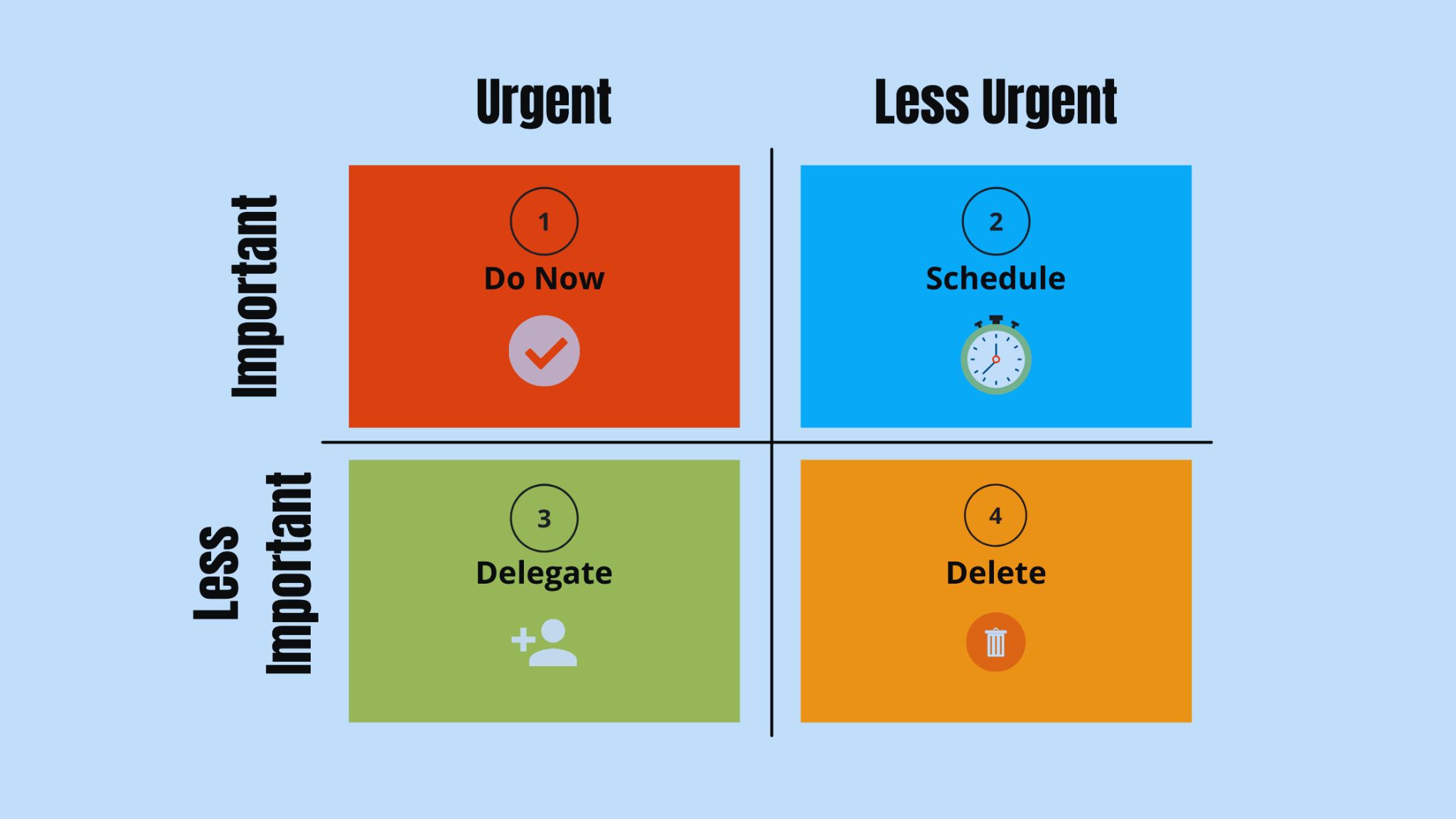
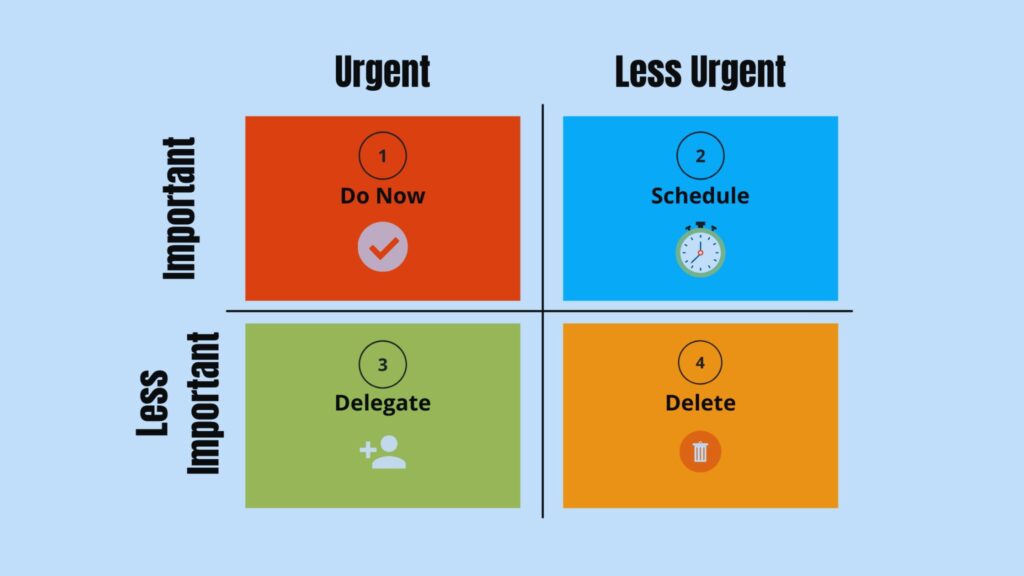
The Eisenhower Matrix, which is also commonly referred to as the Urgent-Important Matrix, helps individuals and organizations by sorting out their tasks according to their urgency and their importance. This matrix would be divided into quadrants in an attempt to distinguish these quadrants into four parts:
Quadrant 1: Urgent and Important – Matters needing urgent attention, or attached to consequences of quite a large magnitude in case those tasks are not done. These can sometimes be referred to as crisis situations or close deadlines.
Quadrant 2: Not Urgent but Important – This includes things that are relevant toward your long-term goals but whose completion need not be urgently addressed. Such activities include planning, personal growth, and building relationships.
Quadrant 3: Urgent but Not Important – These are tasks that are urgent; that is, they must be done immediately, but they are not important in terms of contributing to the achievement of one’s long-term objectives. They are classified as either distractions or interruptions, and the activities that may fall into this group include unscheduled meetings or minor requests.
Quadrant 4: Not Urgent and Not Important – Things that are not urgent and important. Generally, these activities are time wasters and do not serve your goals, like excessive browsing of social media or any other unproductive entertainment.
How to Use the Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix is simple to use, but it does take self-discipline and awareness of one’s self. Here is a step-by-step process on how to use this effective tool:
List your tasks: Write down all the tasks you want to accomplish-both personal and professional.
Categorize Your Tasks: After having listed your tasks, place each of them into one of four quadrants based on whether it is urgent or important.
Prioritize: First, focus on the things in Quadrant 1 because these are both urgent and important. After that, give as much time as possible to Quadrant 2 tasks, for while less pressing, these are important in the long run. Keep to a minimum, or better still, relegate when possible tasks in Quadrant 3, and eliminate or cut down drastically the time spent on Quadrant 4 activities.
Review and Adjust: Periodically review your task list and modify it as necessary. Over time, you should work toward minimizing the number of tasks that fall into Quadrant 1 by focused planning and working on Quadrant 2 tasks.
The Significance of Quadrant 2: A Gateway to Work-Life Balance
Quadrant 2 is where the magic happens. While tasks in this quadrant are not urgent, they are crucial in achieving long-term success and personal satisfaction. This includes activities like exercise, education, relationship building, and strategic planning.
Now, for work-life balance, the important quadrant to engage time with is Quadrant 2. It’s the avenue you have where you can invest in those activities that would prevent burnout and build sound relationships with the right people and enhance general well-being. By consistently devoting time to Quadrant 2, you create a buffer that reduces the number of crises-that is, Quadrant 1 tasks-and helps maintain a harmonious balance between work and personal life.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
With all its great power, Eisenhower Matrix is not without its challenges. Following are some common pitfalls and strategies to avoid them:
Procrastination: You might be putting off the important tasks just because they are not urgent. Putting off important tasks because they aren’t urgent will build up a store of tasks in Quadrant 1. Schedule regular time blocks for Quadrant 2 activities.
Overcommitting: Doing too much often leads to too many activities crowding into Quadrant 1. Practice saying no to non-essential requests and delegate when appropriate.
Neglecting Quadrant 2: Most people have a tendency to pay too much attention to urgent tasks at the expense of Quadrant 2. Move it to the top of your priority list to invest time daily in Quadrant 2 activities.
Misclassification: This is easy, especially when emotions get involved. You need to be honest with yourself and critically assess each task in terms of its importance and urgency.
Real-World Applications of the Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix is not some theoretically developed model, but rather a method put into practice by many highly successful individuals and organizations around the world. The following are examples of real-world applications:
Personal Time Management: The Eisenhower Matrix is used for prioritizing daily activities, maintaining focus on what really matters to make one’s life more balanced and successful.
Project Management: This matrix is used by teams in managing the priorities of project activities for effective resource utilization and timely completion of work projects without unnecessary stress.
Crisis Management: Organizations utilize this matrix in times of crisis to identify urgently needed actions and what might be deferred or delegated.
Leadership Development: Long-term strategy and personal development are the priorities leaders should focus on so as not to be bogged down by firefighting day in and day out.
The Eisenhower Matrix and Work-life Balance
Work-life balance is an important constituent of general well-being. This is the actual seat of the Eisenhower Matrix, where you really have to assess what is truly important and make very conscious choices as to where you are to lay investments of time and energy.
Consistently using the Eisenhower Matrix gives you the opportunity to verify that you are not just reacting to urgent needs but also include activities in your agenda that would bring long-term happiness and success. The approach does not burden you with stress, rules out the notion of burnout, and thus leads to a much fuller life, at work and in personal life.
How to Use the Eisenhower Matrix: Step by Step
How to make this practice a reality? Let me guide you through how you can apply the Eisenhower Matrix into your daily life:
Begin with a Brain Dump: This involves writing down, on a weekly basis, all the things you need to do. It could range from your tasks at work to your personal commitments and even the tiniest of errands.
Quadrant categorization of tasks: Take your list and run through, placing each in one of the four quadrants. Be honest about what is truly important versus what is just urgent.
Scheduling Your Week: After you have assigned the quadrant, schedule your week. Allow time for Quadrants 1 and 2; pay extra attention to make sure time is made for the important but not urgent tasks.

Daily Review This is done every day’s end. Jotting down unfinished tasks in the next day’s space and re-categorizing the quadrant categories appropriately will remind you of unfinished tasks.
Weekly Reflection Take time at the end of the week to reflect on what’s working and what’s not. Change your approach for the following week.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Getting used to a new time management system can sometimes be quite overwhelming, especially if you’re used to doing things in a different way. Here’s how to overcome the most common resistance:
Start Small: Begin to implement the Eisenhower Matrix for only one day or just a week. Increase your usage of the matrix as you get comfortable.
Stay Consistent: The first and foremost success factor of the Eisenhower Matrix is consistency. Stick to it, no matter how weird it may feel the first several times. Eventually, it will be ingrained in your thinking.
Seek Accountability: Share your goals with a friend, colleague, or coach. Having someone to hold you accountable can make a big difference in staying on track.
Reward Yourself: Celebrate your successes no matter how small. Among other things, celebration of small victories may serve as a good motivator that will help crystallize good habits.
Case Study: The Eisenhower Matrix in Action
Let’s take a closer look at a case study to understand exactly how the Eisenhower Matrix works in a real scenario:
Case Study: Sarah’s Path to Work-Life Balance
Sarah is the marketing manager at a medium-sized company. The same as many professionals, she faced the problem of time management and could hardly stand up to demands from work. She was always putting out fires-quadrant 1 tasks-and had little time for strategic planning or personal development-quadrant 2 tasks.
Once Sarah learned about the Eisenhower Matrix, she decided to give it a try. She started by listing all her tasks for the week and categorizing them into the four quadrants. She realized that she spent a lot of time on Quadrant 3 tasks, which consisted of urgent but not important activities, like responding to non-essential emails and attending meetings that didn’t add value.
By purposely choosing to delegate some of these and decline others, Sarah freed up more time for Quadrant 2 activities. She began investing more time in strategic planning and team development that lowered the number of crises experienced but also helped her do her job better.
In a few months, Sarah got the right balance in her life. She was less stressed, more productive, and had adequate time for her family. The Eisenhower Matrix changed her perspective about working and living.
Long-Term Benefits of the Eisenhower Matrix
Applying the Eisenhower Matrix in life may result in considerable long-term effects, especially in trying to balance work and personal life. Some of the major benefits that it offers are discussed here:
1. Enhanced Productivity
The prime benefit of using the Eisenhower Matrix is that your productivity will increase manifold times automatically. You categorize your tasks into urgent and important slots; therefore, you will invest your time and energy only in things that really count. This translates to good work performance and an equally good personal life. Over time, by applying the habit of prioritizing, in essence, you will be able to deliver more in less time, hence having ample time to take your mind off your concerns and engage in leisure activities for personal fulfillment.
2. Reduced Level of Stress
Stress usually comes with the sensation of being swamped with countless urgent things that need to be done. The Eisenhower Matrix helps you regulate this, allowing you to keep your attention on what is truly important so that the crises demanding your immediate attention decrease. The more time you spend up-front in Quadrant 2 activities-planning and personal development-the fewer situations will develop into emergencies. Doing this proactively not only increases your output but also greatly reduces the levels of stress.
3. Better Decision Making
The Eisenhower Matrix enhances your decision-making power because you will need to think critically about the importance and urgency of each task. This eventually develops great discernment in you between what is essential and what is not so that you will be able to make sound decisions both at work and in personal life. You have clarity to invest more resources in their effective use so that all of your efforts are focused on long-term goals and values.
4. Better Work-Life Balance
The most coveted benefit of the Eisenhower Matrix is certainly a healthy work-life balance. By focusing on things that are important but not urgent-which includes spending time with loved ones, enjoying your hobbies, and keeping healthy-you will give way to a more balanced lifestyle. In the process, you ensure success in professional life along with satisfaction in personal life. The result is a more holistic sense of well-being and satisfaction.
5. Long-Term Success
Ongoing utilization of the Eisenhower Matrix builds a strong foundation for success that can last a lifetime. By focusing on tasks that stimulate your growth and development, you are strategically placing yourself for continued success. Whether it is career advancement, building stronger relationships, or an achievement of another personal nature, the Eisenhower Matrix keeps you ever forging ahead positively. This is often key in achieving lasting success and happiness.
Adapting the Eisenhower Matrix to Different Contexts
The beauty of the Eisenhower Matrix is that it can be adapted really well. Even though it is very common in personal time management, it will do nicely even in team management, project planning, and even life goals. Now, let’s take a closer look at how you can refine the matrix to suit the different areas of your life.
1. Workplace Application
The Eisenhower Matrix can be used professionally to iron out the workflows, give priority status to tasks, and manage projects with teams. Managers are able to encourage their teams to categorize different tasks according to the matrix so that everyone is aligned with what is most important. It enhances not just the productivity of personnel but the efficiency of the entire team. At this stage in project planning, teams may apply the matrix to identify tasks that are urgent and need immediate focus, and those tasks that require focus in the long term-for instance, Quadrant 1 and Quadrant 2, respectively.

2. Personal Development
The Eisenhower Matrix serves as an asset for setting and achieving long-term objectives in personal development. Classification of personal undertakings or activities enables one to work persistently toward self-improvement. You can use the matrix to highlight the type of activities you’re doing like reading, exercise, and skills development that are key to personal growth but generally don’t have a deadline. As long as you’re continually addressing these Quadrant 2 activities, you are making steady progress on your personal development.
3. Family and Relationships
This is where it gets tough, though–trying to balance family life against work. The Eisenhower Matrix balances that by prioritizing important family activities: quality time with your loved ones, attending events in your home, and putting in quality time to keep healthy relationships. This ensures family remains paramount in your life. This emphasis on Quadrant 2 activities helps prevent the neglect of personal relationships that are so crucial for long-term happiness and fulfillment.
4. Health and Well-being
Health tends to suffer in the daily grind of life, but long-term, it is an investment that cannot be ignored. In this respect, health-related activities can be listed in order of priority by using the Eisenhower Matrix, such as regular exercising, eating healthily, and preventive health care. By adopting these as your daily routine, you ensure your physical and mental state are not compromised. This proactive approach to health helps prevent crises, quadrant 1, and contributes to a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Common Misconceptions about the Eisenhower Matrix
Despite its simplicity and effectiveness, a number of fallacies about the Eisenhower Matrix make it not be well executed as it should be. Let’s look at some of those misconceptions:
1. It’s Only for Work Tasks
One of the myths would be that this Eisenhower Matrix applies only to work-life tasks. In fact, it could be applied to each and every sector of life: personal development, health, relationships, and leisure. Setting priorities using the matrix in every sphere will promise a more well-rounded and fulfilling life altogether.
2. All Urgent Tasks Are Important
Another myth is the one that suggests everything urgent is important; that again, is not true. Many tasks seem urgent yet are not important in the light of overall scenarios. The Eisenhower Matrix distinguishes between tasks that are truly critical and others which, though urgent, are unimportant. Concentrate on what’s really important, and you will avoid the urgency trap.
3. Quadrant 4 Activities Are Always Bad
Whereas Quadrant 4 things-those things that are not urgent and not important-are often thought of as time wasters, not all downtime is bad. In order to keep the mind and body fresh, rest, relaxation, and leisure activities are necessary. The key is to be intentional about how you spend your downtime. Instead of mindlessly scrolling through social media, consider activities that will rejuvenate you, such as reading, being in nature, or practicing mindfulness.
4. One-Size-Fits-All Solution
The Eisenhower Matrix has universality, yet it’s not another one-size-fits-all kind of solution. It needs to be adjusted according to your particular circumstances, goals, and lifestyle. For some individuals, some tasks are going to be more urgent or important than they will be for others. The key is in adjusting the matrix to reflect your priorities and also to review and adjust them periodically.
Evolving with the Eisenhower Matrix: How to Keep on Evolving into the Future of Time Management by Jaleh Hakami
The demands on your time and energy continue to grow as we journey deeper into the 21st century. The Eisenhower Matrix is one of those timeless tools that will evolve with these demands, helping you stay focused and keep your eyes on the ball in an increasingly chaotic world. Here’s how you can continue to evolve with the matrix:
1. Go digital
While it is a simple tool, modern technology gives a number of aides to the Eisenhower Matrix. There are a lot of apps and digital tools that can help you apply this matrix more effectively. You can categorize your tasks as per priority, set reminders, and track progress using such tools, which make it much easier to ensure you never fall behind on your priorities.
2. Be Flexible
Life is unpredictable, and priorities can change in a split second. The Eisenhower Matrix wants you to be flexible because you can reassess your tasks from time to time and alter them. In one way or another, priorities will constantly be shifting throughout your life, but the matrix will help to realign you toward your goals.
3. Integrate with Other Productivity Systems
Meanwhile, the Eisenhower Matrix can be mixed with other productivity systems, like the Pomodoro Technique, GTD, or the 52/17 Rule. You will be able to integrate those into an overall time management strategy for maximizing your efficiency and work-life balance.
4. Commit to Lifelong Learning
The final key to making the Eisenhower Matrix work for you in the long run is through a commitment to lifelong learning and personal growth. As you develop new skills, experience, and grow, both personally and professionally, this matrix will leverage those newer challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion: The Eisenhower Matrix as a Lifetime Friend
The Eisenhower Matrix is more than a time management tool; it could be a lifelong companion that helps one maneuver through the trials and tribulations of modern life. One can choose tasks based on how urgently they are needed and how important they are. This, in turn, lets you be very conscious about what sphere of your life needs the time and energy investment. It enhances your productivity, contributes to a healthier work-life balance, and makes life more fulfilling.
Live with the Eisenhower Matrix, and you’ll be better prepared to deal with demands at work and life in general.